ACID/BASE CHEMISTRY TRIVIA + QUIZZES
Interesting Questions, Facts, and Information
 Acids and Bases
Acids and Bases
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids, Bases and You! |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| Acids and Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |
| High School Acids & Bases |

ACID-BASE CHEMISTRY
For thousands of years people have known that vinegar, lemon juice and many other foods taste sour. However, it was not until a few hundred years ago that it was discovered why these things taste sour - because they are all acids. The term acid, in fact, comes from the Latin term acere, which means "sour". While there are many slightly different definitions of acids and bases, in this lesson we will introduce the fundamentals of acid/base chemistry.
In the seventeenth century, the Irish writer and amateur chemist Robert Boylefirst labeled substances as either acid or bases (he called bases alkalies) according to the following characteristics:
Acids taste sour, are corrosive to metals, change litmus (a dye extracted from lichens) red, and become less acidic when mixed with bases.
Bases feel slippery, change litmus blue, and become less basic when mixed with acids.
While Boyle and others tried to explain why acids and basesbehave the way they do, the first reasonable definition of acids and bases would not be proposed until 200 years later.
Acids are substances which produce hydrogen ions in solution.
Bases are substances which produce hydroxide ions in solution.
Neutralisation happens because hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions react to produce water.
![]()
![]()
Limitations of the theory
Hydrochloric acid is neutralised by both sodium hydroxide solution and ammonia solution. In both cases, you get a colourless solution which you can crystallise to get a white salt - either sodium chloride or ammonium chloride.
These are clearly very similar reactions. The full equations are:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In the sodium hydroxide case, hydrogen ions from the acid are reacting with hydroxide ions from the sodium hydroxide - in line with the Arrhenius theory.
However, in the ammonia case, there don't appear to be any hydroxide ions!
You can get around this by saying that the ammonia reacts with the water it is dissolved in to produce ammonium ions and hydroxide ions:
![]()
![]()
This is a reversible reaction, and in a typical dilute ammonia solution, about 99% of the ammonia remains as ammonia molecules. Nevertheless, there are hydroxide ions there, and we can squeeze this into the Arrhenius theory.
However, this same reaction also happens between ammonia gas and hydrogen chloride gas.
![]()
![]()
In this case, there aren't any hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions in solution - because there isn't any solution. The Arrhenius theory wouldn't count this as an acid-base reaction, despite the fact that it is producing the same product as when the two substances were in solution. That's silly!
An acid is a proton (hydrogen ion) donor.
A base is a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor.
The Relationship Between Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry
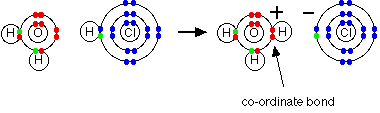
The Bronsted-Lowry theory doesn't go against the Arrhenius theory in any way - it just adds to it. Hydroxide ions are still bases because they accept hydrogen ions from acids and form water. An acid produces hydrogen ions in solution because it reacts with the water molecules by giving a proton to them. When hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in water to produce hydrochloric acid, the hydrogen chloride molecule gives a proton (a hydrogen ion) to a water molecule. A co-ordinate (dative covalent) bond is formed between one of the lone pairs on the oxygen and the hydrogen from the HCl. Hydroxonium ions, H3O+, are produced.
| |
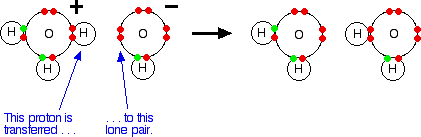
When an acid in solution reacts with a base, what is actually functioning as the acid is the hydroxonium ion. For example, a proton is transferred from a hydroxonium ion to a hydroxide ion to make water.
Showing the electrons, but leaving out the inner ones:
It is important to realise that whenever you talk about hydrogen ions in solution, H+(aq), what you are actually talking about are hydroxonium ions. | |
- Neutralization reaction occurs, when equal quantities of acids and bases occurs. For example: H+ ions react with OH- ions, to make the H2O molecule.
Conjugate acid - base pairs
have chemical formula that differ by one H+ (they differ by both one H atom and by a +1 charge). They typically appear in a chemical equation for an acid-base reaction, where one is a reactant and the other is a product. Stronger acids have weaker conjugate bases, while stronger bases have weaker conjugate acids. The strongest acids have conjugate bases that are so weak as to be non-basic. The strongest bases have conjugate acids that are so weak as to be non-acidic.